Treatment for Neuropathic Pain
amrtiyaayuclinic@gmail.com
Dec 26, 2024 07:46 PM
Peripheral neuropathy refers to a group of conditions that damage the peripheral nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms. These nerves transmit signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. The Ayurvedic perspective on peripheral neuropathy differs from modern medicine, focusing on the balance of the body’s doshas, or energies.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy in Ayurveda
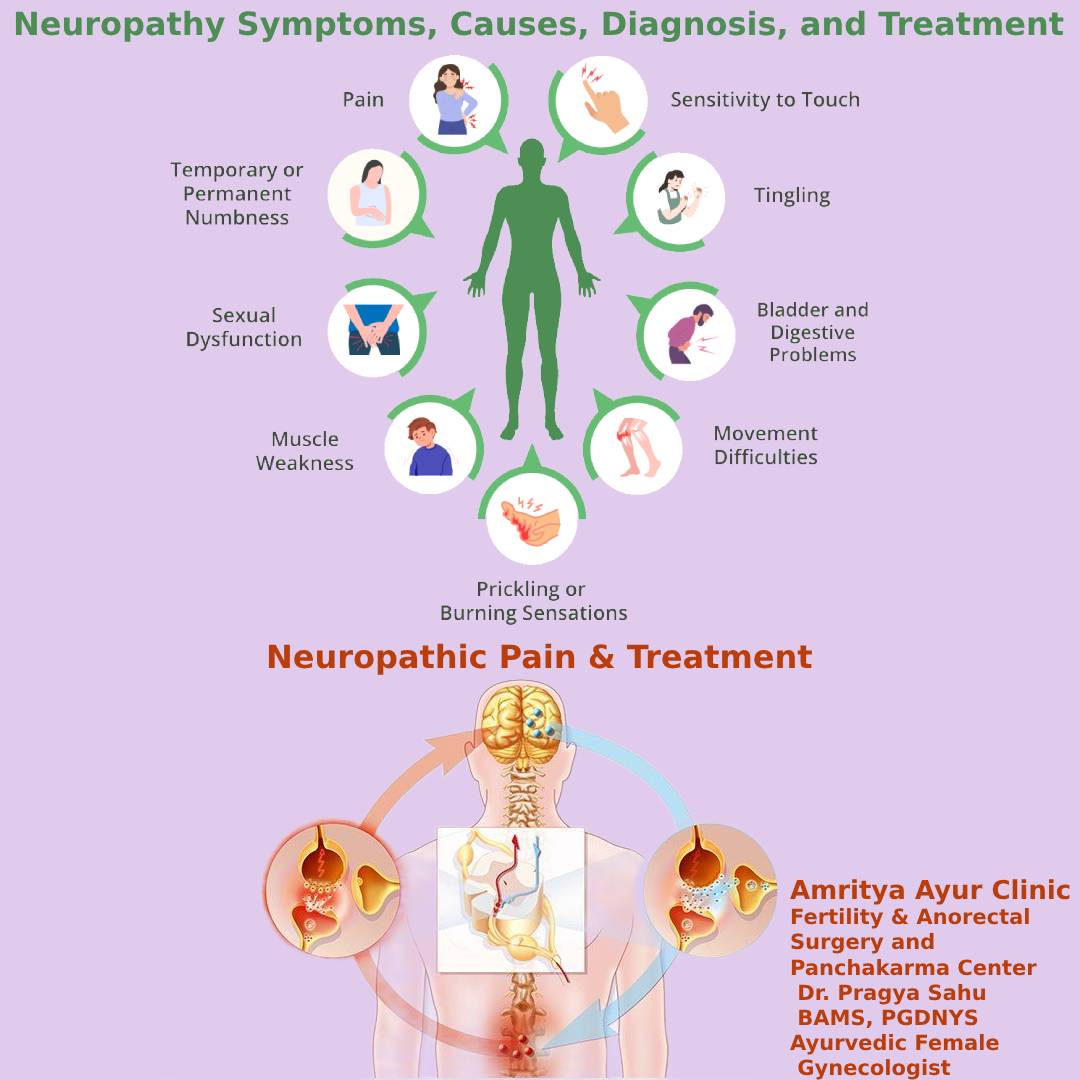
In modern medicine, common symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
- Numbness and tingling (often in hands and feet)
- Pain (sharp, burning, or throbbing)
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of coordination
- Sensitivity to touch
- Increased risk of injury or infection
In Ayurveda, symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can manifest as imbalances in the Vata dosha (which governs movement and sensation). The symptoms may include:
- Numbness (Sensation loss): Often described as a feeling of heaviness or lack of energy in the limbs.
- Pain (Shoola): A burning, sharp, or stabbing pain in the affected areas, particularly in the limbs.
- Tingling or Pricking Sensation (Like ants crawling): This can be a manifestation of vitiated Vata.
- Weakness and stiffness in the muscles and joints.
- Difficulty in movement and balance issues may arise as the motor nerves are affected.
- Dry skin, hair fall, and brittle nails could also be secondary signs.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy in Ayurveda
According to Ayurveda, peripheral neuropathy is caused by an imbalance of the Vata dosha, especially when it is aggravated by factors such as:
-
Vata-Vitiating Factors: Excessive dry, cold, or rough conditions aggravate the Vata dosha. This can result from poor dietary habits, lack of proper nutrition, or excessive physical strain.
-
Dietary and Lifestyle Factors:
- Poor Diet: Excessive consumption of cold, dry, and processed foods leads to the depletion of Ojas (vital essence) and the weakening of the nerves.
- Overexertion: Excessive work, mental strain, lack of rest, or improper posture can also disturb the Vata balance.
- Toxins (Ama): Accumulation of Ama (toxins) from improper digestion can lead to the obstruction of channels, including the nervous system, causing nerve damage.
-
Diabetes (Madhumeha): This is one of the most common modern causes of peripheral neuropathy. In Ayurveda, it is thought to be caused by an imbalance in Kapha and Vata doshas, with poor digestion leading to the formation of Ama, which circulates and weakens the nerves.
-
Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma, whether from accidents or repetitive strain, can directly impact the nerves and lead to neuropathy.
-
Other Underlying Conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure (Raktagata Vata), nutritional deficiencies (e.g., B12 deficiency), and alcohol abuse also contribute to nerve damage.
Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy in Ayurveda
Diagnosis in Ayurveda is based on a thorough assessment of the patient's physical, emotional, and lifestyle habits, along with a detailed examination of the pulse (Nadi Pariksha), tongue (Jihva Pariksha), and other body signs.
-
Pulse Diagnosis (Nadi Pariksha): Vata vitiation is usually detected by the irregularities or uneven pulses, especially in the wrist area.
-
Examination of the Doshas: The doctor evaluates the imbalance between Vata, Pitta, and Kapha doshas. In the case of peripheral neuropathy, Vata is usually aggravated.
-
Patient History: A detailed history of the patient’s lifestyle, diet, and any other pre-existing medical conditions (e.g., diabetes) is assessed.
-
Tongue and Body Examination: The appearance of the tongue (e.g., dry, cracked, pale, or coated) and the overall body condition (e.g., weakness or stiffness) are important indicators.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy
Ayurvedic treatment for peripheral neuropathy aims to balance the Vata dosha, eliminate toxins (Ama), improve circulation, and rejuvenate nerve function. It consists of dietary changes, herbal remedies, lifestyle modifications, and therapies that pacify Vata and strengthen the nervous system.
-
Dietary Recommendations:
- Consume warm, moist, and nourishing foods that are easy to digest. Soups, stews, and warm teas help balance Vata.
- Include healthy fats (like ghee, olive oil, and sesame oil) to nourish the nervous system.
- Avoid cold, dry, and spicy foods that aggravate Vata.
-
Herbal Remedies:
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): A well-known herb for calming Vata and rejuvenating the nervous system. It helps to improve muscle strength and reduce nerve inflammation.
- Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Known for its cognitive and nerve-strengthening properties. It aids in mental clarity and alleviates nerve pain.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce pain and inflammation in the nerves.
- Jatamansi (Nardostachys jatamansi): Often used to calm Vata and ease nervous tension, it also supports the regeneration of nerves.
- Vacha (Acorus calamus): Known for improving circulation and enhancing the functions of the nervous system.
-
Panchakarma Therapy:
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Regular full-body oil massage with warm, Vata-pacifying oils (such as sesame oil) can soothe nerve pain and reduce stiffness. It also improves circulation and restores balance to the nervous system.
- Shirodhara: This treatment involves pouring warm oil over the forehead and is considered very beneficial for calming the mind and nervous system, especially in cases of stress-related neuropathy.
- Basti (Enema therapy): Specialized enemas can be used to detoxify the body, especially in cases of Ama (toxins) accumulation affecting the nervous system.
- Nasya (Nasal Therapy): Administration of medicated oils or powders through the nasal passages can help cleanse and balance the head and neck region, improving nerve function.
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Proper Rest: Ensure adequate sleep and avoid physical and mental stress to allow the body to heal.
- Yoga and Pranayama (Breathing exercises): These can be extremely effective in improving circulation and calming Vata. Poses that focus on stretching and strengthening the legs and hands are especially beneficial.
- Routine: Establishing a daily routine (Dinacharya) that includes regular meal times, exercise, and relaxation helps keep Vata in balance.
-
Detoxification: If Ama (toxins) is present, Ayurveda recommends Ama pachana (detoxification) therapies. These help cleanse the body, remove accumulated waste, and rejuvenate the tissues, including the nerves.
Conclusion
In Ayurveda, the treatment of peripheral neuropathy revolves around balancing the Vata dosha, eliminating toxins, improving digestion, and rejuvenating the nervous system. With personalized treatments involving diet, herbs, Panchakarma therapies, and lifestyle adjustments, Ayurveda aims to restore the body's natural balance, alleviate symptoms, and support overall nerve health. However, as with any condition, Today consult with Amritya Ayur Clinic for best treatment.